Nowadays, there are countless projection screen brands on the market, leaving consumers overwhelmed. A mix of imported and domestic brands flood the market, with varying quality levels. Prices range from a few hundred yuan to several hundred thousand yuan, making it difficult for consumers to decide. Even many consumers have the misunderstanding that “using a screen is almost the same as projecting onto a white wall.” In fact, all of this stems from a lack of understanding of projection screens.
Moreover, recently many people have sent private messages asking how to choose a projector screen. Although choosing a screen is less technically demanding than choosing a projector, it’s still hard to explain it in one sentence. So I’ve compiled the latest 2025 projector screen selection guide. If you’re currently choosing a screen, spend a few minutes reading this article before making a purchase—it’s worth it.
1. Common Screen Types and Their Advantages
1.1 Electric Screens
Electric screens can be retracted and extended electrically. They use a tubular motor to store the flexible screen material and are equipped with a wireless remote control function.Advantages: Electric storage saves space; with reasonable layout, it can be used together with a TV; almost all screen materials can be made into electric screens, making them the most popular type among users, though the price is slightly higher.

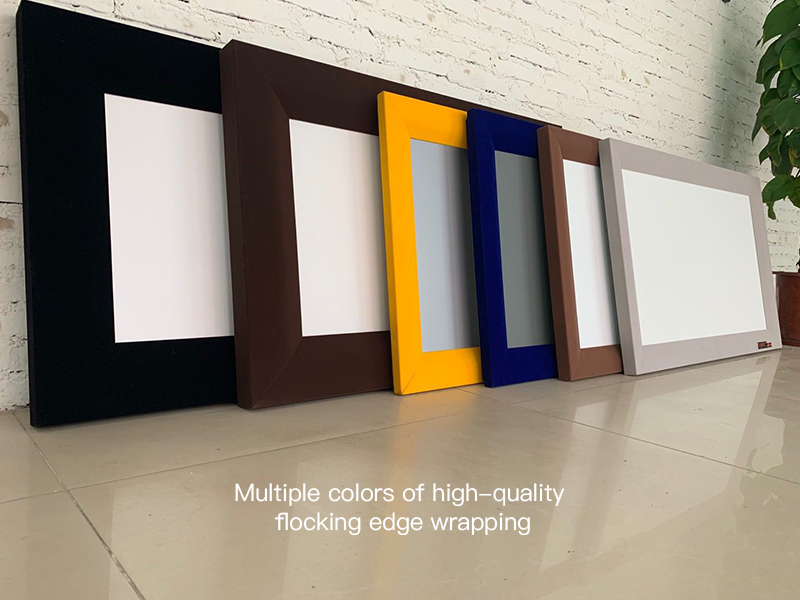
1.2 Frame Screens
Frame screens look like picture frames, usually with aluminum flocked borders. The screen material is in the middle, and springs are used around the edges to fix the screen in place.Advantages: Excellent flatness, and the cost is lower than that of electric screens.
1.3 Glass Fiber Screens
Glass fiber screens use a base fabric woven from glass fibers, with a coating on the surface. They are usually slightly rigid and not very soft.Advantages: Good basic gain and high-quality imaging.

1.4 Soft Screens
Soft screens are made of PVC material with a direct surface coating, and the material is relatively soft.Advantages: Good imaging effect.

1.5 White Plastic Screens
White plastic screens usually use a base fabric woven from textile threads, with a coating on the surface. The grid pattern of the woven fiber threads can be seen on the surface.Advantages: Low cost, affordable price, intuitive imaging effect, and wide viewing angle.

1.6 Metal Screens
Metal screens have a special metal coating sprayed on their surface. Currently, most commercial cinemas use metal screens. However, metal screens have high costs, and their surface coatings are relatively fragile.Advantages: High gain and excellent imaging effect.
2. Screen Characteristics by Color
Let’s look at projector screens classified by color—they are generally divided into white screens and gray screens. Gray screens reduce the brightness performance of projectors, have a smaller viewing angle than white screens, affect grayscale performance, and cause inaccurate color temperature and gamma values. Therefore, white screens are more suitable for home use.
3. Screens Classified by Optical Properties
Acoustics are of little significance for home projectors, so we won’t analyze them here. Let’s focus on optical properties—screens can be divided into ordinary screens and anti-light screens. Anti-light screens are mainly used with ultra-short-throw projectors. Although there are also long-throw anti-light screens now, their effect is not very good.
4. Screens Classified by Aspect Ratio
By aspect ratio, screens are generally divided into three types: 4:3, 16:9, and 2.35:1. The 4:3 aspect ratio is mainly used in scenarios such as office meeting rooms for presentations; for home use, 16:9 is sufficient; only a few movies and TV programs use the ultra-wide 2.35:1 aspect ratio, which is rarely used in daily life.


